Reverse a singly linked list.
Java Solution 1 – Iterative
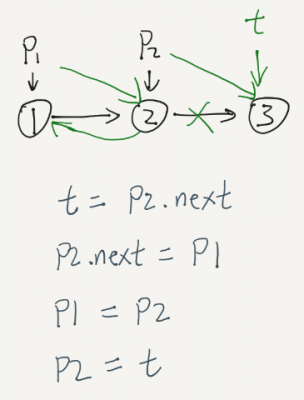
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { if(head==null||head.next==null) return head; ListNode p1 = head; ListNode p2 = p1.next; head.next = null; while(p1!=null&& p2!=null){ ListNode t = p2.next; p2.next = p1; p1 = p2; p2 = t; } return p1; } |
Java Solution 2 – Recursive
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { if(head==null || head.next == null) return head; //get second node ListNode second = head.next; //set first's next to be null head.next = null; ListNode rest = reverseList(second); second.next = head; return rest; } |
–
Solved in a much cleaner solution. See also execution example below.
Code:
Node reverse(Node n)
{
Node first = null;
while(n != null)
{
Note next = n.next;
n.next = first;
first = n;
n = next;
}
return first;
}
Execution example:
Input:
1->2->3->4
n 1 2 3 4 null
next 2 3 4 null
first 1 2 3 4
Output:
4->3->2->1->null
A simpler recursive solution to this can be like below
reverseList(ListNode node, ListNode prevNode) {
if (node == null) {
return prevNode;
}
Node prevNextNode = node.next;
node.next = prevNode;
return reverseList(prevNextNode, node);
}
just check for p2
Yes, kushi, you’re right!
Its the corner condition.
+1
while(p1!=null&& p2!=null){
why not
while(p2!=null){
No, its not the same when you reach the end of the list. At the end of list p1 points to the last element and p2 points to null, when || is used the condition becomes true and you get NPE when p2.next is executed
Hi Lin,
you are right!
it calls again and again right..when next line second.next execute??
here we are calling reverseList(second)..So,when next line execute??
String foo = "bar";
A more concise version. Is there a reason why use second, and keep it before recursion. This will work, too.
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode rest = reverseList(second);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return rest;
}
Actually, it’s the same.
while(p1!= null && p2!= null){ //Should be || instead of &&.