Here are a set of diagrams to illustrate Java String’s immutability.
1. Declare a string
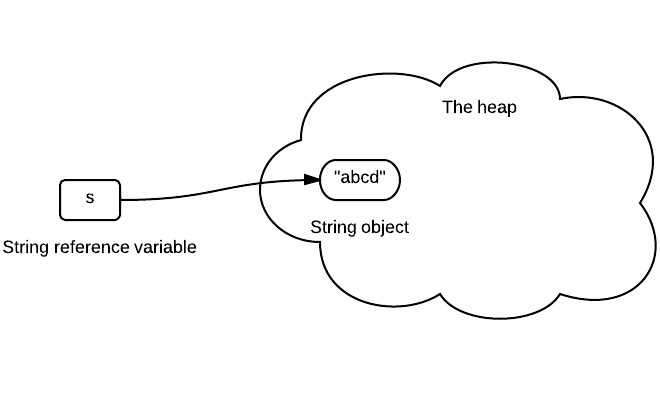
The following code initializes a string s.
String s = "abcd"; |
The variable s stores the reference of a string object as shown below. The arrow can be interpreted as “store reference of”.
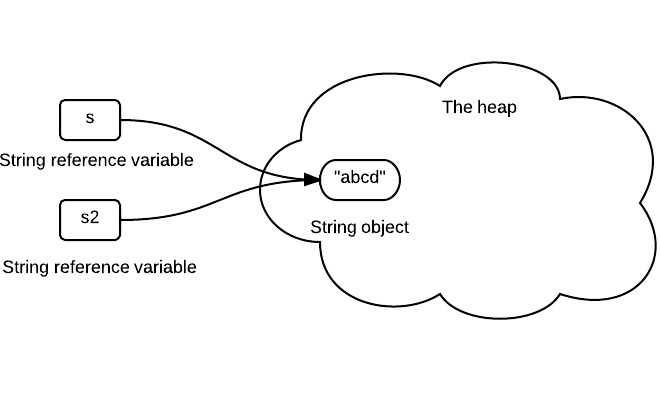
2. Assign one string variable to another string variable
The following code assign s to s2.
String s2 = s; |
s2 stores the same reference value since it is the same string object.
3. Concat string
When we concatenate a string “ef” to s,
s = s.concat("ef"); |
s stores the reference of the newly created string object as shown below.
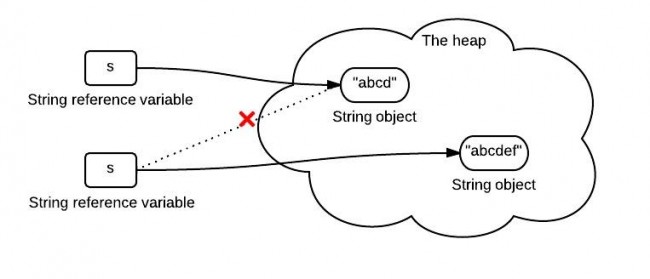
In summary, once a string is created in memory(heap), it can not be changed. String methods do not change the string itself, but rather return a new String.
If we need a string that can be modified, we will need StringBuffer or StringBuilder. Otherwise, there would be a lot of time wasted for Garbage Collection, since each time a new String is created. Here is an example of using StringBuilder.
Thanks for writing this wonderful piece. I’m glad I found your website. It helped me a lot. Here is an insightful content on Java. I would be happy if you check that. This will definitely be informative to you.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8_JxMy4Gm04
I never understand the concept of string in java but Now, I understood the concept of string. Thank you sir.
Diagram are simple and explainable.
New Reader of this website.
Happy that now I learn something sensible.
TRUE
s = “abcd”
s = s.concat(“ef”)
2 s
thanks…
I learn Java for year, but only now understood what is it “immutable” String. Thnx
i think that the top “s” in the last diagram should be “s2”.
Why is variable s2 in the third diagram?
Why two s in the last diagram? Where is s2?
顶一个nice article
My bad. I thought I was still on DZone.com (which talks about multiple platforms). This is a Java specific site, so I’ll delete this .Net nonsense.
This diagram works for .Net as well. The only change would be s=s+”ef”;
Thanks very much for pointing out this problem. In JDK 7, it actually crates a new array by using array copy. http://www.programcreek.com/2013/09/the-substring-method-in-jdk-6-and-jdk-7/
source from rt.jar:
substring(beginIndex, count)
return new String(offset + beginIndex, endIndex – beginIndex, value);
// Package private constructor which shares value array for speed.
String(int offset, int count, char value[]) {
this.value = value;
this.offset = offset;
this.count = count;
}
http://www.programcreek.com/2013/04/why-string-is-immutable-in-java/
No, it will creat a new one by using array copy.
the diagram is not very well. String is immutability for perfomance operations like as substring. The string have array of char (value), and offset, count.
s3 = s.substring(0, 1)
s3.value reference to “abcdef” in heap
but s3.offset = 0, count = 1
s3 reference “a”
why did JAVA design String class this way? what is the purpose?