
This module is a native Bluetooth implementation intended to perform fundamental tasks in a communication between Microcontrollers (especially Arduino) and Games/Applications, made with Godot Engine, running inside Android. At the moment this module doesn't support communication between two mobile devices, but such functionality can be added in the future.
The module has been tested with Godot-2.1.x-stable and HC-05/06 Bluetooth module(hardware) on an Arduino Uno R3.
Native Dialog Box Layout;
Easy Implementation Of Custom Layouts Inside Godot.
engine.cfg:
[android]
modules="org/godotengine/godot/GodotBluetooth"[note] The mandatory permissions are already configured. They're:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN"/>To use the module functions on your scripts, start the module as follows:
var bluetooth
func _ready():
if(Globals.has_singleton("GodotBluetooth")):
bluetooth = Globals.get_singleton("GodotBluetooth")
bluetooth.init(get_instance_ID(), true)
And declare the functions you need:
func getPairedDevices(boolNativeLayout):
if bluetooth:
bluetooth.getPairedDevices(boolNativeLayout)
(You can learn more about Singletons and initializations here).
Then use the functions wherever you want, following the API reference below.
[note] The Android and the Microcontroller need to be paired before establishing a connection through this module for communication, you can use the options in the settings of your device to do this. Note that there is a difference between being paired and being connected, to be paired means that two devices are aware of each other's existence, to be connected means that the devices currently share an RFCOMM channel and are able to transmit data with each other.
The following functions are available:
Startup Function
void init(get_instance_ID(), bool bluetoothRequired)The bluetoothRequired is a boolean that tells if the bluetooth is required inside the game/application. If true, the game/application will close when the bluetooth is off and the user refuses to activate on the startup, if false, the game/application will continue in the occurrence of the same situation.
Paired Devices Layout
void getPairedDevices(bool nativeLayout)The nativeLayout is a boolean that tells the module that, if true, you want the Native Layout showing the list of paired devices, if false, you want to build your own Custom Layout inside Godot.
For Custom Layouts Only
void connect(int deviceID)The deviceID is an integer representing the device you want to connect, only when using Custom Layouts you need to use this function, to get the deviceID see the _on_single_device_found on the callbacks section bellow. In summary, when using Custom Layouts you'll create your own visualization screen of paired devices and when the user chooses any of them you'll need to call this function to complete the connection.
Send Data
void sendData(String stringData)
void sendDataBytes(RawArray byteData)The stringData is a string containing the data you want to send, the module will take care of transforming this string into a byte array to perform comunication. The byteData is a raw array, in case you want to send the byte array directly.
Callbacks
_on_data_received(String dataReceived)
_on_disconnected()
_on_single_device_found(String deviceName, String deviceAddress, String deviceID)
_on_connected(String deviceName, String deviceAddress)
_on_connected_error()The dataReceived is a string containing the data sended by the Microcontroller. On the _on_single_device_found, the deviceName, deviceAddress and deviceID are the informations found about each of the paired devices individually, as the Android bluetooth adapter finds them (see the GodotBluetoothDemos folder for an example of use), the same variables on the _on_connected shows the information about the device that has been connected after the user make a choice.
Further Information And Demo Projects
For complete examples of usage for both Native Layout and Custom Layout, see the GodotBluetoothDemos folder.

REMEMBER: You need to compile the module and add the binaries in the examples as per the instructions at the beginning of this file so that the examples work!
The circuit used in the demos is quite simple, and can be seen below:
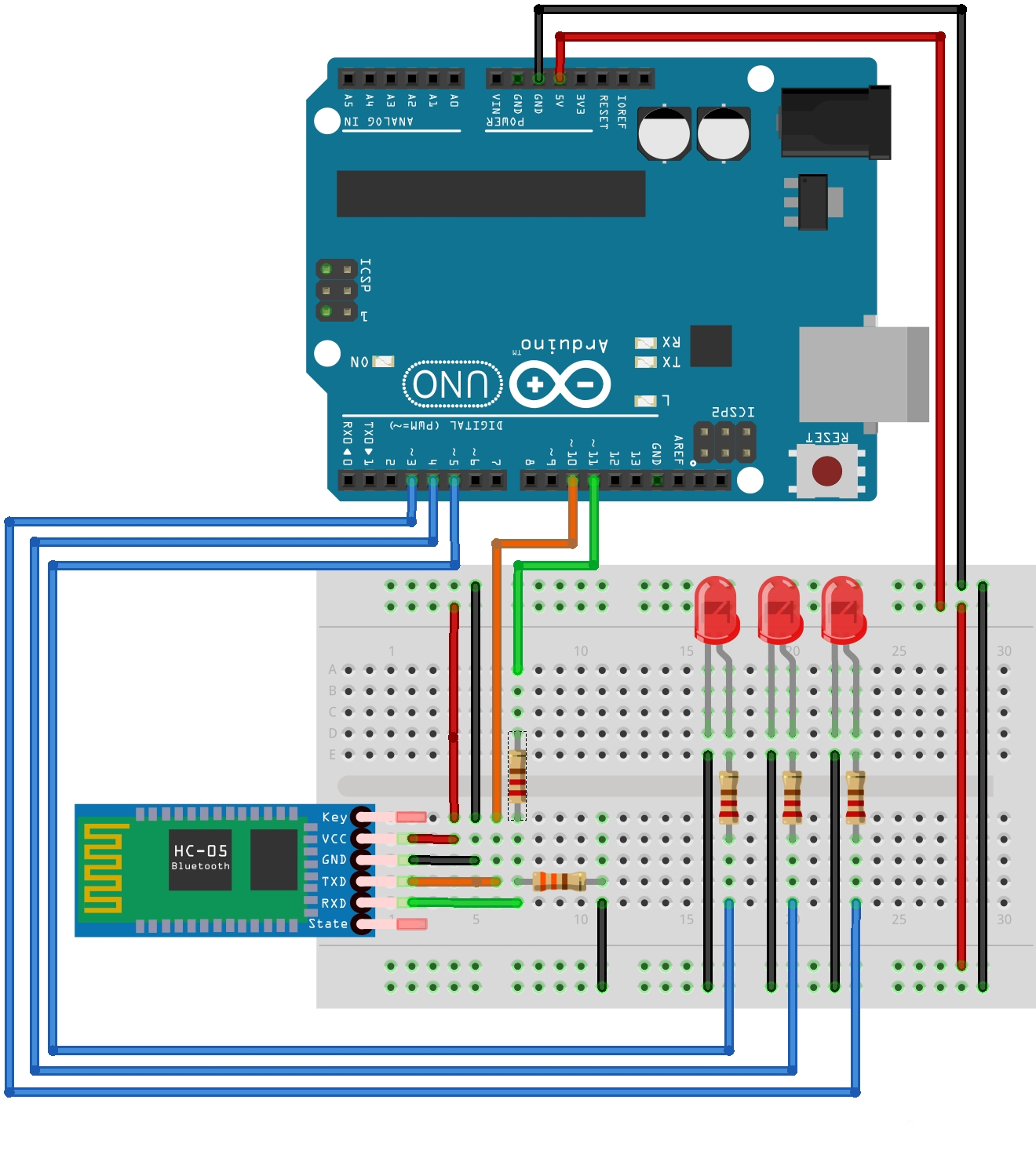
The file bluetoothExample.ino containing the code used in Arduino, can be found inside the GodotBluetoothDemos/Arduino folder.
Be creative! =)