Given the following perfect binary tree,
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
After calling your function, the tree should look like:
1 -> NULL
/ \
2 -> 3 -> NULL
/ \ / \
4->5->6->7 -> NULL
Java Solution 1 – Simple
public void connect(TreeLinkNode root) { if(root==null) return; LinkedList<TreeLinkNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<TreeLinkNode>(); LinkedList<Integer> depthQueue = new LinkedList<Integer>(); if(root!=null){ nodeQueue.offer(root); depthQueue.offer(1); } while(!nodeQueue.isEmpty()){ TreeLinkNode topNode = nodeQueue.poll(); int depth = depthQueue.poll(); if(depthQueue.isEmpty()){ topNode.next = null; }else if(depthQueue.peek()>depth){ topNode.next = null; }else{ topNode.next = nodeQueue.peek(); } if(topNode.left!=null){ nodeQueue.offer(topNode.left); depthQueue.offer(depth+1); } if(topNode.right!=null){ nodeQueue.offer(topNode.right); depthQueue.offer(depth+1); } } } |
Java Solution 2
This solution is easier to understand. You can use the example tree above to walk through the algorithm. The basic idea is have 4 pointers to move towards right on two levels (see comments in the code).
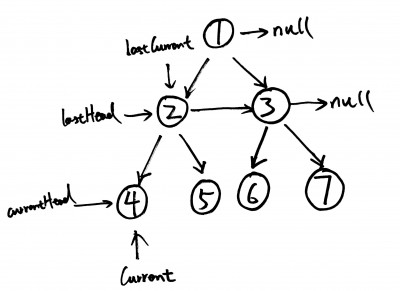
public void connect(TreeLinkNode root) { if(root == null) return; TreeLinkNode lastHead = root;//prevous level's head TreeLinkNode lastCurrent = null;//previous level's pointer TreeLinkNode currentHead = null;//currnet level's head TreeLinkNode current = null;//current level's pointer while(lastHead!=null){ lastCurrent = lastHead; while(lastCurrent!=null){ if(currentHead == null){ currentHead = lastCurrent.left; current = lastCurrent.left; }else{ current.next = lastCurrent.left; current = current.next; } if(currentHead != null){ current.next = lastCurrent.right; current = current.next; } lastCurrent = lastCurrent.next; } //update last head lastHead = currentHead; currentHead = null; } } |
in your first solution that second if statement (
if(root!=null)) is redundent.But that would not be constant extra space. It would require O(log(n)) space where n are the number of nodes in the tree. The question specifically mentions no extra space.
Thanks for the solution!
I came up with this solution which seems more easily understandable.
public void connect(TreeLinkNode root) {
// only in edge case where there is no tree
if (root == null) return;
//By induction this will be the leftmost node in the current level
TreeLinkNode cur = root;
//By induction this will be the leftmost node in the next level
TreeLinkNode left = root.left;
//check if this is the last level
if (left == null) return;
//tranverse the current level linking all nodes in the next level
while(cur != null){
//link left and right child of the current node
cur.left.next = cur.right;
//link right child of current node and left child of next node
if (cur.next != null){
cur.right.next = cur.next.left;
}
//progress
cur = cur.next;
}
//move to next level
connect(left);
}
Do a typical level by level binary tree traversal using a queue. When you encounter that the level is changed, navigate from the queue and update next pointers.