This is a classic interview question which confuses novice Java developers. In this post I will use an example and some diagram to demonstrate that: Java is pass-by-value.
1. Some Definitions
Pass by value: make a copy in memory of the actual parameter’s value that is passed in.
Pass by reference: pass a copy of the address of the actual parameter.
Java is always pass-by-value. Primitive data types and object reference are just values.
2. Passing Primitive Type Variable
Since Java is pass-by-value, it’s not hard to understand the following code will not swap anything.
swap(Type arg1, Type arg2) { Type temp = arg1; arg1 = arg2; arg2 = temp; } |
3. Passing Object Variable
Java manipulates objects by reference, and all object variables are references. However, Java doesn’t pass method arguments by reference, but by value.
Question is: why the member value of the object can get changed?
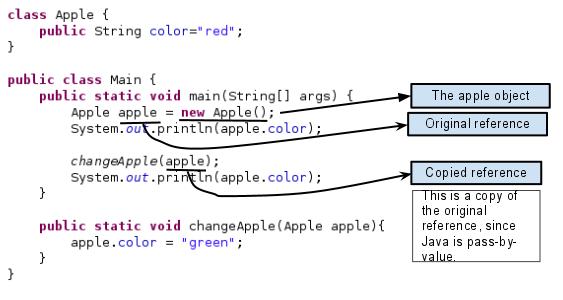
Code:
class Apple { public String color="red"; } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Apple apple = new Apple(); System.out.println(apple.color); changeApple(apple); System.out.println(apple.color); } public static void changeApple(Apple apple){ apple.color = "green"; } } |
Since the orignal and copied reference refer the same object, the member value gets changed.

Output:
red green
but when I write
double d = 3.14;
is ‘d’ not essentially a reference to the value being stored mysteriously in memory? Is there really any difference between these situations? This almost seems like an exception that handles primitives differently from Objects.
Need to cover the case for array, both primitive array as well as object array, which behaves like object.
This concept is very easy, but difficult to put into words.
Java is always pass by value. Confusion on this topic arises when object references are used as arguments, but the reference is still pointing to the same object. In other words, when a parameter or argument is passed in Java, it is simply copied in a new location that acts as placeholder for the value.
To conclude, Java passes the value of reference, which allows it to pass by value at its core. For more information and examples on this topic please view this guide: https://itinterviewguide.com/java-pass-by-value/. Let me know if it explains the concept clearly 🙂
what is the difference between http://www.programcreek.com/2013/09/string-is-passed-by-reference-in-java/ that one and this post?
When we say
A a = new A();
The new operator allocates memory for the created object and returns a reference to that memory which is then assigned to the variable of the class type.
So, it can be said “a†is a variable which is holding a value and that value happens to be the reference to the memory address. So even for object it is pass by value.
Please see the post to know more –
http://netjs.blogspot.com/2015/04/java-pass-by-value-or-pass-by-reference.html
YES, but values are not necessarily references, think about it before posting, thanks.
object reference are just values, so it’s pass by reference.